BITCOIN ???
Is it a peer to peer payments system, is it digital gold, is it a hedge against inflation, or is it truly the purest form of sound money…It’s a little bit of all that and we will attempt to explain it to you.
The idea of attaching monetary value, or value of any kind, to a string of alphanumeric code would seem to be the most counterintuitive of concepts. However, as one studies more and more about Bitcoin it can be seen that, perhaps, it is possible for it to be a form of money. Money has changed radically over time. In the past value was attached to sea shells, huge stones ( the Rai stones of the Yap islands), salt and, of course, gold. In the current age of computers and a world of interconnectedness, many of the old forms of money are becoming, or have already been superseded. Bitcoin as the primary cryptocurrency, just might be money for the digital age.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
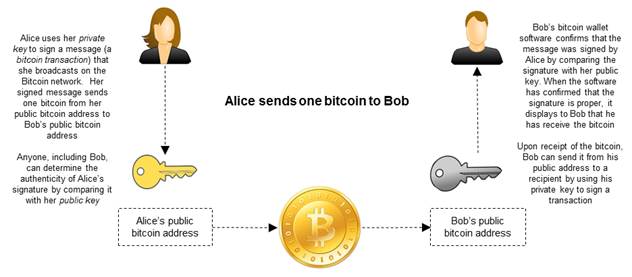
Bitcoin is essentially a decentralized public ledger that records and validates all transactions that take place on its blockchain. The public ledger means that anyone can see how much a particular wallet is holding and what activity is going on in that wallet. The ledger is freely available for all to peruse at their leisure. However, to whom that wallet belongs is not revealed. Many people think that Bitcoin is anonymous, but you can see that it is not as all records are publicly available back to the very first transaction. It is better to call the system psuedo-anonymous as we don’t need personal details attached to the Bitcoin wallet address.
To put bitcoin into a wallet on the blockchain is easy. All you need is a public key (the Bitcoin address) and you can send bitcoin to that address and the bitcoin will arrive. It may take 10 minutes or so as the bitcoin miners confirm your transaction to ensure that you have the funds you claim to be moving. This process, the confirmation of the transaction on the blockchain, is needed as it prevents you from sending your bitcoin to multiple parties – what was termed the double spend problem.
However, to spend the bitcoin, that is to send it to another wallet, you need the private key that corresponds to the public key. Without this your bitcoin will languish in the blockchain forever. This has already happened to several people. The fact that you need a private key to use your bitcoin, and that this private key is, in the current state of technology, secure, means you have a safe store of value that you can send and receive over borders, without third parties, securely and swiftly.
WHO SECURES THE NETWORK?
You might well ask: ‘What is the incentive for the people who maintain this decentralized public ledger?” The answer is that they are rewarded with bitcoin. For – and this is very simplified – making sure all the transactions are accurately recorded and stored the miners are, if they get a certain mathematical puzzle correct, given some bitcoin. In addition there is also a small fee attached to bitcoin transactions that is skimmed off by the miners to cover costs associated with their work. Hence, Bitcoin is a self sustaining network. Currently, the Bitcoin network is the most powerful computer system on Earth with thousands of individual computers securing the blockchain. Importantly, it is also decentralized. By this I mean that, unlike a bank, it is not done by a single entity or corporation, but simultaneously worked on by computers around the world. Just because one computer, one country or one continent is cut off from the network does not affect the network’s ability to work. Bitcoin is safe from such dangers as it is independent of governments and politics.
THE KEY FEATURES OF BITCOIN
Bitcoin’s independence is important for a number of reasons:
Firstly, it is peer to peer. By this I mean that you can send and receive bitcoin without going through a third party. This may seem trivial until a government decides you are a subversive for protesting about something and closes your account.

Secondly, Bitcoin is not inflationary. That is to say, the supply of Bitcoin is limited and known. The governments of countries often print their way out of trouble, but ultimately this only means fiat currencies lose value. Look at any currency against gold over the last 100 years and you will find that it has lost value. There may be arguments for inflation, but none would argue that high inflation is a good thing. Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 000 000 ( Each bitcoin is comprised of 100 000 000 satoshis ) and inflates, slowly, until that number is reached. Currently around 19 000 000 bitoinns have been minted/created. No one can create more than the determined 21 000 000, the programme on which bitcoin is built is unchangeable.

Finally, Bitcoin is a universal store of value. In theory it could provide the world with a store of value that transcends borders, is freely transmissible and is immune to the temporal influences of politics, wars and civil unrest. It can be an anchor in troubled times and not subject to the whims and fancies of short sighted economic interests or governments inflating their currencies out of debts.

Bitcoin has its own issues. The vast wealth it has generated for a minority of early investors is probably not the healthiest of starting points, nor is the complexity of use assisting its adoption. Ultimately, as a form of money, it is as absurd as any other – sea shells, the Yap stones, silver, gold, dollars or pounds – or as logical. Money is a peculiar thing, what works for different ages and societies works. We were already drifting away from solid gold and silver in the 1950s and by the end 1971 the gold standard disappeared in the US. Meaning you could no longer redeem your dollar bill for gold. There is an argument that Bitcoin fulfills the requirements demanded by today’s global economy, that it solves some of the issues surrounding the abuse of the creation of money, that it could act as a force for the good by taking power away from central banks and that it could allow people who do not have access to bank accounts to trade freely across borders or within them. It is a subject worth looking into and familiarizing yourself with.
For those wishing to pursue the topic further, Micheal Saylor’s Academy and 101 bitcoins provide some good insights:
For a short youtube introduction go to:
Those wishing to seriously study Bitcoin and its history should look at www.saylor.org
Go to: Start Learning and put in bitcoin, then go to “Bitcoin for Everybody”. It is an interesting introduction to the topic and gives a good picture.

